When ice a solid melts it turns into water a liquid. The Heat of fusion is denoted by Δl.

Latent Heat Of Fusion And Vaporization Specific Heat Capacity Calorimetry Physics Youtube
The enthalpy of fusion of a substance also known as latent heat of fusion is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy typically heat to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a solid to a liquid at constant pressureFor example when melting 1 kg of ice at 0 C under a wide range of pressures 33355 kJ of energy is absorbed with no temperature.

Specific latent heat of fusion of ice formula. Specific latent heat of fusion 334 kJkg from the table above specific latent heat of fusion 334 1000 334000 Jkg. If m kg of the solid changes into the liquid at a constant temperature which is its melting point. This equation states that the heat Q that must be added or removed for an object of mass m to change phases.
The latent heat of fusion is the change from liquid to solid. In the figures above is given below. If you have 106 grams of ice how much heat in joules would you need to provide to completely melt.
This means that 1g of ice absorb 335 J of energy to become liquid. Specific latent heat of fusion Here is the formula. The specific heat of fusion is similar to the latent heat of fusion since the melting of a given solid at normal pressure generally needs heat energy.
The temperature of the substance changes from t 1 low temperature to t 2 high temperature the heat which the material absorbs or releases is expressed as Q mc Δt Q mc t 2 t 1 The total amount of heat absorbed or liberated by the material is Q mL mc Δt. Takes in and its mass. L is the specific latent heat of fusion for that material.
Substituting the value of m and the specific latent heat. Influence of heat losses on the determination of the specific latent heat of fusion of ice water Specific heat of fusion is the heat of fusion to be added per unit mass of a solid to be melted. There are 2 processes involve when an ice is converted into water at 25C.
If you apply heat to ice it will melt. ΔHf is the heat of fusion. It is the change in the heat of ice when it changes from solid to liquid that is ice to water.
So the formula tells us how much heat energy is needed to go into a material to change it from a solid to a melted liquid. M mass of the substance. Thus the latent heat of fusion encompasses the process of adding heat to melt some solid.
L fracQ M Where Q amount of heat. The heat of fusion formula is given as. Specific latent heat of fusion of water 334 000 Jkg.
This is called fusion. The temperature stays at 0ºC H 2 O s energy à H 2 O l So in order to calculate the heat of fusion of ice we need to know how much heat it. Thus the latent heat of fusion of ice is defined as the amount of heat required to change one gram of ice from 0 degree Celsius to water at 0 degree Celsius.
E h m x l. Note that the temperature does not actually change when matter changes state so its not in the equation or needed for the calculation. At the point when the heat of fusion is referenced to a unit of mass it is typically called the specific heat of fusion while the molar heat of fusion alludes to the enthalpy change per measure of substance in moles.
How much heat energy is required to change 05 kg of ice at 0C into water at 25C. The formula for Latent heat of fusion. The latent heat of fusion is the enthalpy change of any measure of substance when it dissolves.
The literature value for the specific heat of fusion of ice is therefore somewhat lower with q f 334 kJ kg. Formula for Latent Heat. Q mΔH f.
The Formula for Latent Heat. Then the heat absorbed by it means the latent heat of fusion formula will be Q m times L_f. The latent heat is given by the equation.
The formula to calculate heat of fusion is. Consider for example specific latent heat of ice. Except for melting helium heat of fusion is always a positive value.
Thermal energy 05 334000 1670000 J 167 kJ Measuring. The unit of latent heat is Jkg-1 The value of latent heat is variable. This is the amount of energy released when water is melting at 0 C.
The known value for the latent heat of fusion of ice is 80 caloriesgram so the measured value below compares pretty well. The accepted value for the latent heat of fusion of ice is 335 Jg. For example If we want to change ice to water a specific amount of heat is required which will be dependent upon the heat of fusion of ice and amount of water present.
E h means energy equals m for mass times l. Ice at 0C ----- Water at 0C ----- Water at 25C. Latent heat of fusion is defined as the amount of heat required to change a unit mass of a substance from the solid-state to a liquid state at a constant temperature.
Q is heat energy. Specific heat capacity of water 4200 Jkg K Answer. We denote Individual latent heat by L.
The three states of matter are solid liquid and gas. Q 05 Kg 334 KJKg 167 KJ 167000 J. L specific latent heat of fusion of substance.

Solved We Did The Lab Of Latent Heat Of Fusion Of Ice An Chegg Com

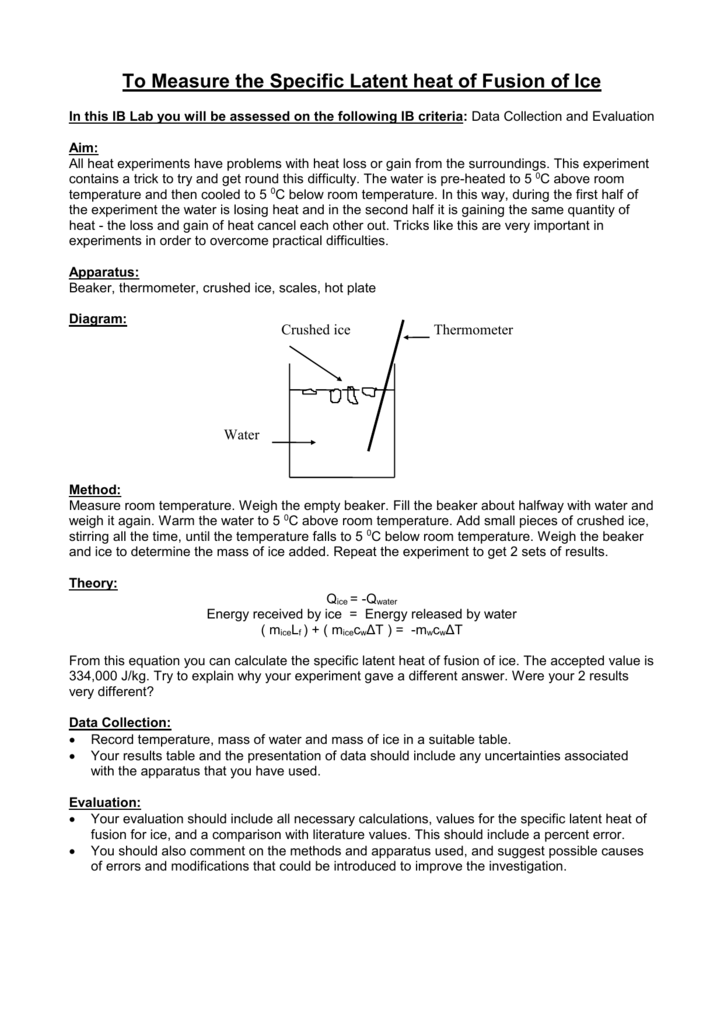
To Measure The Specific Latent Heat Of Ice By Direct Heating Physics Homework Help Physics Assignments And Projects Help Assignments Tutors Online
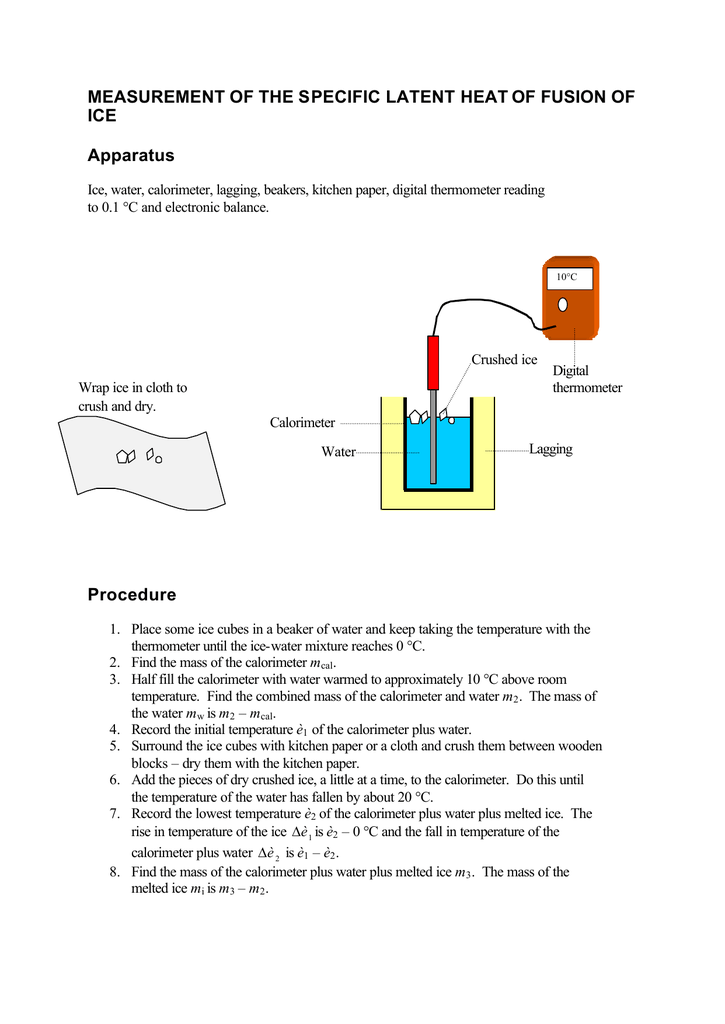
Measurement Of The Specific Latent Heat Of Fusion Of