A bP. By substituting demand and supply formula to the given example equilibrium quantity and price can be calculated.

Calculating Equilibrium Price Definition Equation Example Macroeconomics Class Video Study Com
How to Calculate Equilibrium Price and Quantity 1 Calculate Supply Function.

How to find equilibrium price with supply and demand. Demand formula QD a- bp. The quantity willing supplied by the producers is higher than the quantity demanded by the consumers. A is the intercept of the demand and supply curves.
To find where QS Qd we put the two equations together. The equilibrium price is considered the optimal price as it is the price level at which neither consumers nor suppliers enjoy an advantage or suffer a disadvantage relative to the other. Now that youve mastered demand and supply equations its time to put them together to determine the equilibrium price and quantity in a market.
QS mP b. 2 Calculate Demand Function. Here the equilibrium price is 6 per pound.
B is the slope of two curves. The equilibrium price and quantity in a market are located at the intersection of the market supply curve and the market demand curve. Supply formula QS a bp.
20-2P -10 2P. C dP. How to determine supply and demand equilibrium equations.
While it is helpful to see this graphically its also important to be able to solve mathematically for the equilibrium price P and the equilibrium quantity Q when given specific supply and demand curves. The tool was designed to help you calculate the equilibrium price and quantity for any linear quantity and supply functions both dependants on the price written as. It occurs where the demand and supply curves intersect.
Qs -10 2P. Based on the demand and supply curve the market forces drive the price to its equilibrium level. 1 Excess Demand or 2 Excess Supply Excess supply is the situation where the price is above its equilibrium price.
4 Plug your equilibrium price into either your demand or supply function or both--but most times it will be easier to plug into supply and solve for Q which will give you equilibrium quantity. In the supply and demand model the equilibrium price and quantity in a market is located at the intersection of the market supply and market demand curves. If you have only the demand and supply schedules and no graph you can find the equilibrium by looking for the price level on the tables where the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied are equal again the numbers in bold in Table 1 indicate this point.
The equilibrium price and quantity is the point where the supply and the demand curves intersect. The competitive equilibrium price is determined at the point of intersection of the market demand and the market supply curve. The equilibrium price for dog treats is the point where the demand and supply curve intersect corresponds to a price of 200.
Similar to the supply function we can calculate the demand function with the help of a. If for instance your given the supply function and the demand function and we know that an equilibrium price is only reached when quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded we can easily solve for the equilibrium price. Solution for Discuss how the equilibrium price and quantity change when a change in demand occurs and the supply stays constant and when a change in supply.
In its most basic form a linear supply function looks as follows. The point at which supply and demand levels meet or intersect is the point of both equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price. There are two possibilities.
Finding Equilibrium with Algebra. The price that makes quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied is called the equilib rium price. In other words it is the demand and supply quantities at price zero.
Q D 100 P where Q D represents the quantity demand and P is the equilibrium price and. Note that the equilibrium price is generally referred to as P and the market quantity is generally referred to as Q. When solving for equilibrium price and quantity you need to have a demand function and a supply function.
Consumers demand and suppliers supply 25 million pounds of coffee per month at this price. Qd 20 2P. Consider an economy with the following demand and supply equations.
At the point of intersection the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied in the market which implies that there is no excess supply or excess demand in the market. This can be calculated by ΔQ ΔP. Where P refers to the equilibrium price.
Let us suppose we have two simple supply and demand equations. When we combine the demand and supply curves for a good in a single graph the point at which they intersect identifies the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.
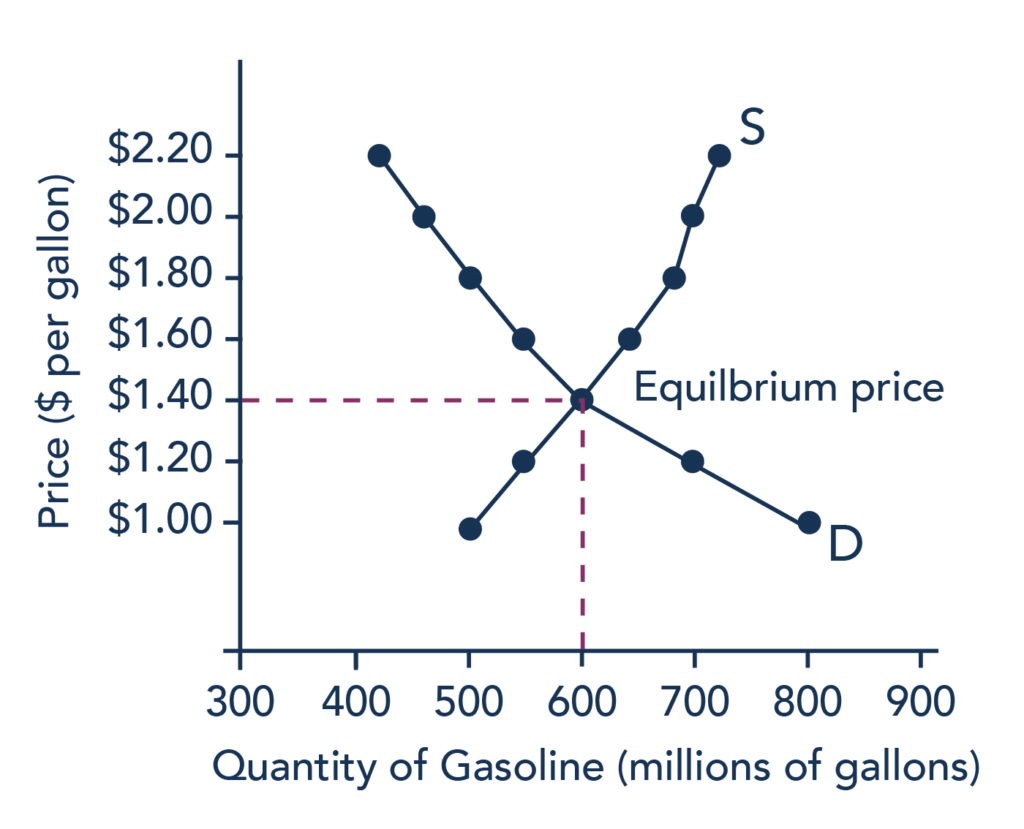
Equilibrium Price And Quantity Introduction To Business

Finding Equilibrium Price And Quantity Using Linear Demand And Supply Equations Youtube

Equilibrium Price And Quantity Introduction To Business
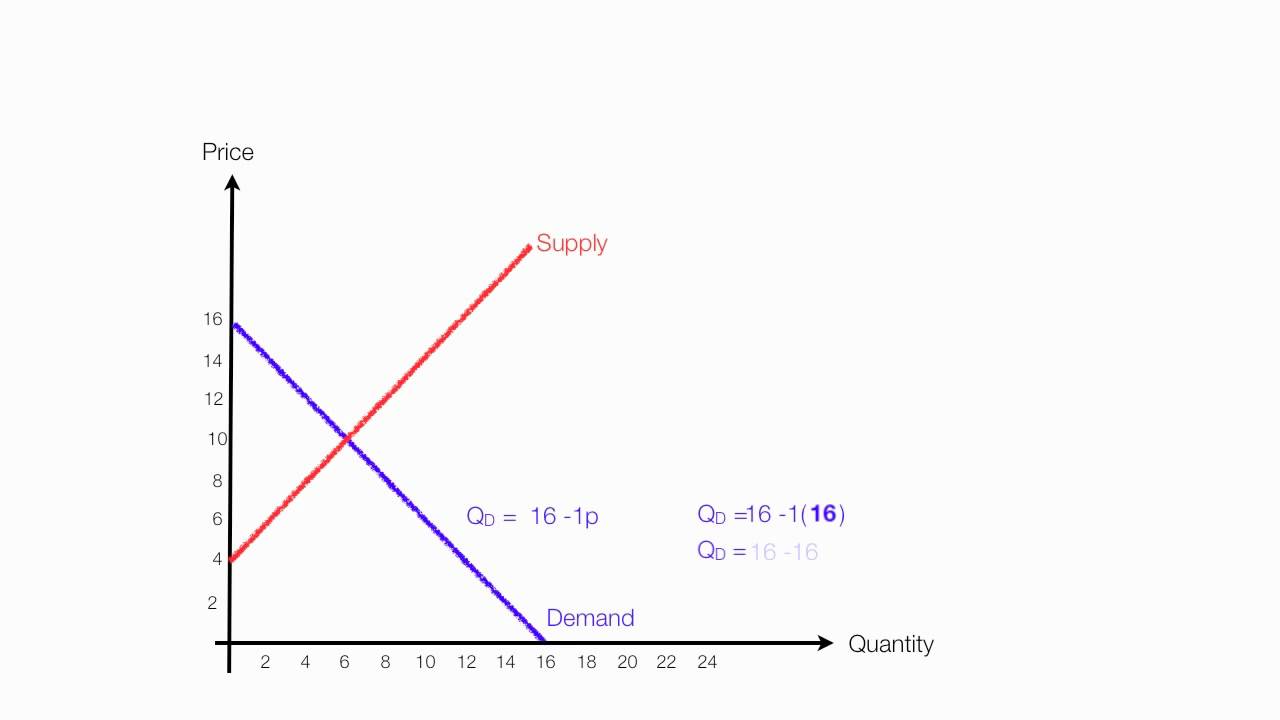
How To Calculate Equilibrium Price And Quantity Demand And Supply Youtube
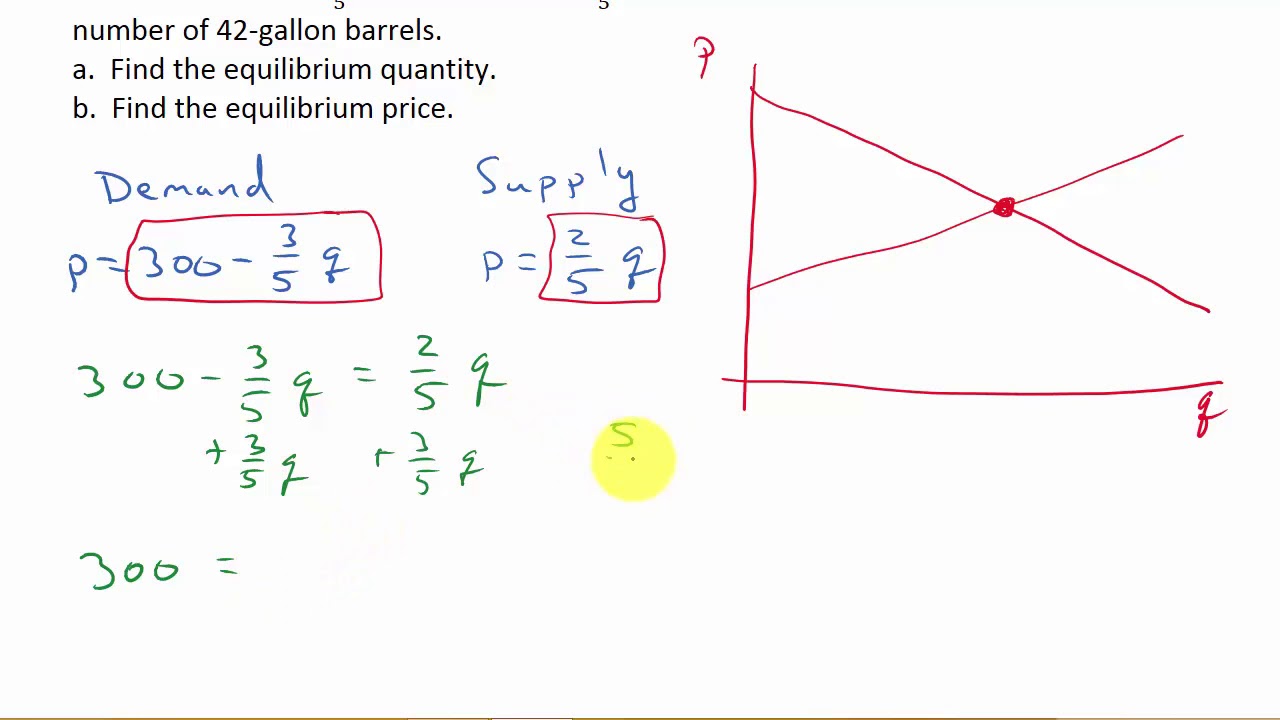
Supply And Demand Finding Equilibrium Quantity And Price Youtube